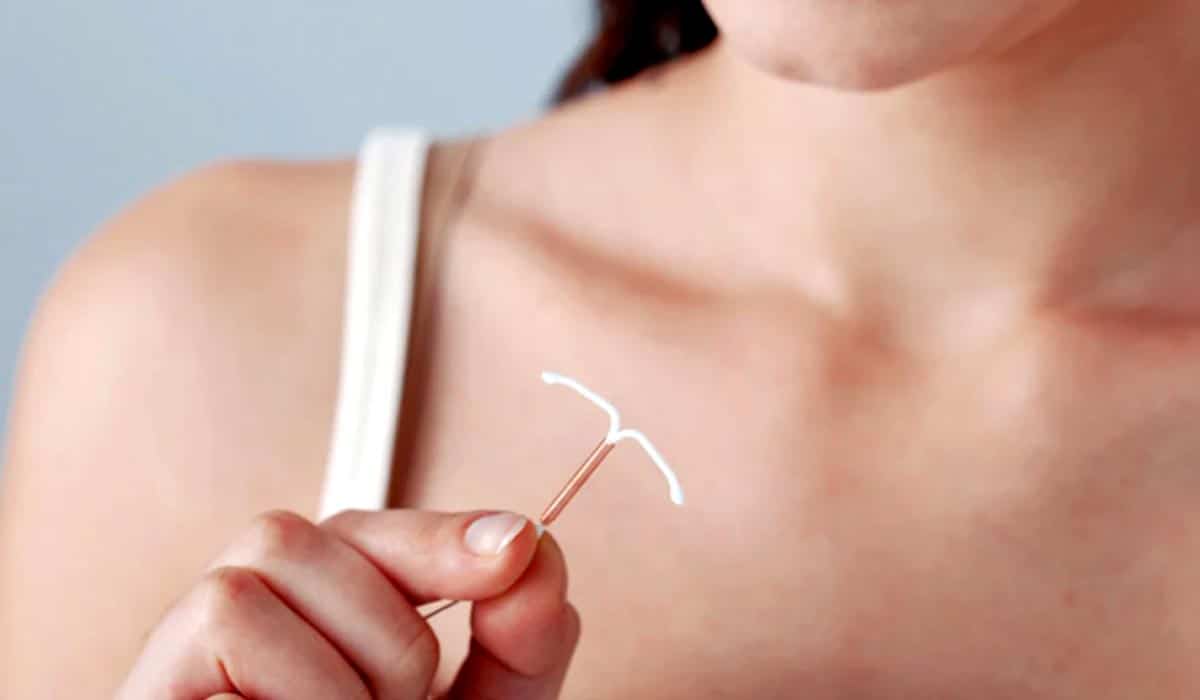
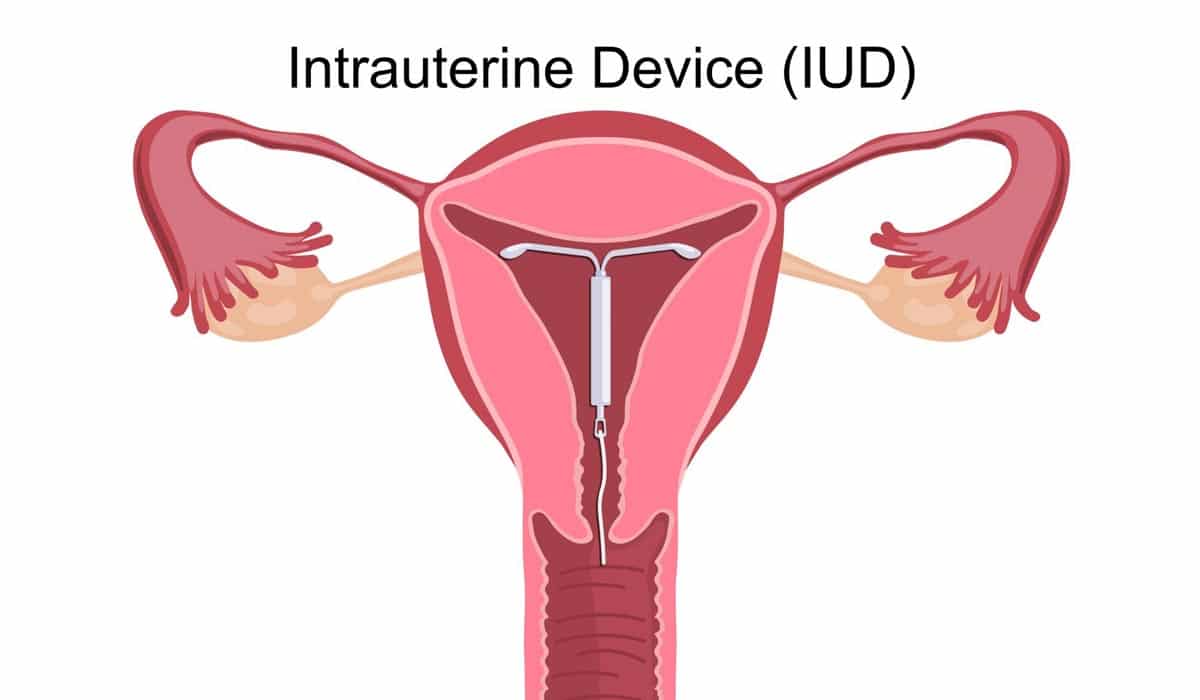
Intrauterine Contraceptive Device (IUD)
An intrauterine device is typically a T shaped device that contains copper and is 100% hormone-free. It is safe to use and has a very high contraceptive effect. The probability of pregnancy in the first year is 0.6 percent with perfect use. They are effective for 5 – 10 years.
Copper IUD
Copper IUDs prevent pregnancy as a result of the combination of the following three mechanisms of action:
- Inhibiting the egg cell (ovum) transport
- Preventing the passage of sperm to the upper genital canal
- Inhibiting fertilization.
It is a good medical practice to take Pap-Smear for cervical cytology before the application of a uterine device.
Application Time

⦁ During menstruation: Copper IUD is easily applied during menstruation when the woman is sure that she is not pregnant.
⦁ After abort practice: IUD can be applied immediately after first trimester spontaneous abortion or within the first week, provided that there are no signs of infection. It is medically unnecessary to wait for menstruation after an abort to apply the IUD. The intervention may be delayed due to the possibility of spontaneous expulsion after second trimester abortions.
⦁ Postpartum application: IUD can be applied within ten minutes after the postpartum placenta is removed, if there is no excessive bleeding at birth and if there is no risk of infection. If it is not applied immediately after delivery, it can be applied within the first two days. Otherwise, the application of the IUD should be postponed until the end of the postpartum 4th week due to the risk of perforation.
Positive Aspects
⦁ It is effective for a long time after application
⦁ They are safe, very effective and reversible methods
⦁ Suitable for breastfeeders
⦁ The use of the method is independent of the timing of sexual intercourse
⦁ Easy to use
⦁ When removed, the return of fertility is not delayed
Negative Aspects
⦁ It is not a suitable method for those at risk of sexually transmitted diseases
⦁ Application and removal requires trained health personnel
⦁ It may cause an increase in menstruation, pain and breakthrough bleeding for a few months after the application
Contraindication
⦁ Pregnancy or suspicion of pregnancy
⦁ Puerperal sepsis
⦁ Immediately after septic abortion
⦁ Those with deformities involving the uterine cavity (congenital anomaly, fibroid, etc.)
⦁ Cervical cancer
⦁ Endometrium cancer
⦁ Current pelvic infections (PID)
⦁ Pelvic tuberculosis
⦁ History of malignant trophoblastic disease
⦁ Undiagnosed vaginal bleeding
Side Effects
IUDs are contraceptive methods that are safe and secure to use when the appropriate case is selected. In the first month following usage, an increase in the amount of menstruation, dysmenorrhea and spotting between menstrual periods can be seen. These symptoms usually disappear after 3-4 months.
Possible complications and actions required to be done:
⦁ Uterus perforation: Very rare
⦁ Pregnancy: While there is an IUD in the uterus, pregnancy may occur very rarely. If the woman wants this pregnancy to continue, IUD is removed. If the pregnancy is in the 1st trimester, it continues.
⦁ Ectopic Pregnancy: IUD never causes ectopic pregnancy, however, it should not be forgotten that ectopic pregnancy can be seen in IUD users, as the IUD does not prevent extra uterine pregnancy even though it prevents intrauterine pregnancy very effectively, and the case should be evaluated well in this respect.
⦁ Pelvic Infection (PID): Pelvic infection, which is a rare and important complication in IUD users, is more common in the first year after administration, but especially in the first 4 months. It is usually seen in those at risk of sexually transmitted diseases (those with polygamous sexual intercourse).
A woman who applied IUD can control herself by feeling the threads in the vagina. It should be said that she may occasionally check, but not too often. It should be stated that the woman who applied IUD should be checked once a year after the first check-up in the following months, but it should be emphasized that if she has anxiety or encounters an unexpected or abnormal situation, it will be appropriate to apply to the clinic immediately. The incidence of expulsion is 3 to 10 percent for IUD in the first year of use.
Warning Signs
⦁ Menstruation delay, suspected pregnancy
⦁ Excessive vaginal bleeding (more than twice of the normal menstrual in terms of duration and amount)
⦁ Abnormal vaginal discharge
⦁ Missing threads, feeling short or long
⦁ IUD removal
⦁ Weakness, fever, shivering, lower abdominal pain
⦁ Abdominal pain, pain during sexual intercourse
Hormonal IUD
Description of the method
MIRENA (Levonorgestrel- releasing intrauterine system) is indicated for:
- Treatment of idiopathic menorrhagia following diagnostic investigation in women and reduction of anemia
- Contraception
- Reduction in dysmenorrhea
- Treatment of endometriosis-related pelvic pain
The method is effective for 5 years. The failure rate is 1 in a thousand. Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious adverse effects on the heart and blood vessels. There is no current evidence of an association between MIRENA use and the development of breast cancer or the progression of subclinical breast cancer.
Mechanism of action
The main effect of hormone IUDs is the local hormonal effect. By preventing endometrial proliferation, it becomes unsuitable for implantation. Sperm’s passage to the uterus is prevented by the thickening of the cervical mucus. Hormone IUDs do not affect ovulation.
Usage
Interval application: LNG-IUD can be applied within the first 7 days of the cycle; no additional method is required. Apart from this, it can be applied at any time when the woman is sure that she is not pregnant, but an additional method (condom or sexual abstinence) should be used for 7 days.
Positive Aspects
⦁ They are safe and very effective
⦁ Protects for a long time
⦁ Recyclable
⦁ Independent of sexual intercourse
⦁ Suitable for breastfeeding women
⦁ Treats menorrhagia complaints, reduces blood loss by 90% during menstruation
⦁ Reduces pelvic infection
Fertility returns immediately when it is removed.
Negative Aspects
⦁ It causes menstrual irregularity, the number of bleeding days increases in the first 6-12 weeks after the application.
⦁ Intermenstrual bleeding may last up to the first 12 months
⦁ Amenorrhea and hypomenorrhea are seen in users in the first year
⦁ It is not a suitable method for those at risk of sexually transmitted diseases
⦁ Application and removal requires trained health personnel on the subject
Eligibility Criteria
Healthy women of all ages (nulliparous or multiparous) can use the IUD as long as they wish, from menarche to menopause. However, the application must be done by a healthcare professional who is knowledgeable, authorized, and experienced. Women at risk of sexually transmitted diseases should definitely use a double method.
Contraindications
⦁ Pregnancy or suspicion of pregnancy
⦁ Current or recurrent pelvic inflammatory disease
⦁ Septic abortion within the previous three months
⦁ Uterine anomalies including fibroids if they distort the uterine cavity
⦁ Breast cancer
⦁ Uterine or cervical malignancy
⦁ Benign or malignant liver tumors
⦁ Recent trophoblastic disease while HCG levels are elevated
⦁ Undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding
⦁ Acute malignancies affecting blood
⦁ Bacterial endocarditis
Side Effects
⦁ Reduction of menstrual bleeding and amenorrhea (57% and 20%)
⦁ Mental status change (4% to 9%)
⦁ Headache (<16%)
⦁ Abdominal distress (<10%)
⦁ Breast tenderness (<10%)
⦁ Acne (6% to 15%)
⦁ Vaginal infection (9% to19%)
⦁ Ovarian cyst (5% to 22%)
⦁ Pruritus (<5%)
⦁ Less than1% postmarketing or case reports acute myocardial infarction, arterial thromboembolism, cerebrovascular accident, deep vein thrombosis, hypersensitivity reaction, increased blood pressure, jaundice, malignant neoplasm of breast, sepsis, venous thromboembolism
Warning Signs
⦁ Menstrual delay
⦁ Weakness, fever, shivering, ongoing lower abdominal pain
⦁ Abnormal vaginal discharge
⦁ Missing threads, feeling short or long
⦁ IUD removal
⦁ Abdominal pain, pain during sexual intercourse
References
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/intrauterine-contraception-candidates-and-device-selection
https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/practice-bulletin/articles/2017/11/long-acting-reversible-contraception-implants-and-intrauterine-devices
https://www.guidelines.co.uk/womens-health/fsrh-intrauterine-contraception-guideline/252622.article
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2770406/
World Health Organization: Intrauterine devices: technical and managerial guidelines for services
World Health Organization. Medical eligibility criteria for contraceptive use 2008 update