Effective Ways to Avoid Gum And Jaw Bone Diseases
Although many people are aware of the risks to dental health posed by gum disease, only a few know that the effects of gum disease go beyond the teeth and gums. They can directly affect the health of the jawbone.
Gum disease is just an infection. If left untreated, it can cause huge oral issues. Fortunately, for better oral health and a healthy smile, restorative dentistry procedures can help reverse the harm caused by gum disease and jawbone loss.
Gum diseases
Diseases of the gum and jawbone are known as periodontal diseases. They are diagnosed or treated by periodontists rather than by general doctors. These diseases may, however, lead to other diseases that are of concern to doctors.
Infections of the teeth, gingivae, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone can spread to other tissues, causing diseases like sinusitis, jaw osteomyelitis, and aspiration pneumonia. Maintaining proper oral health is the single most effective way of preventing the production and progression of periodontal diseases.
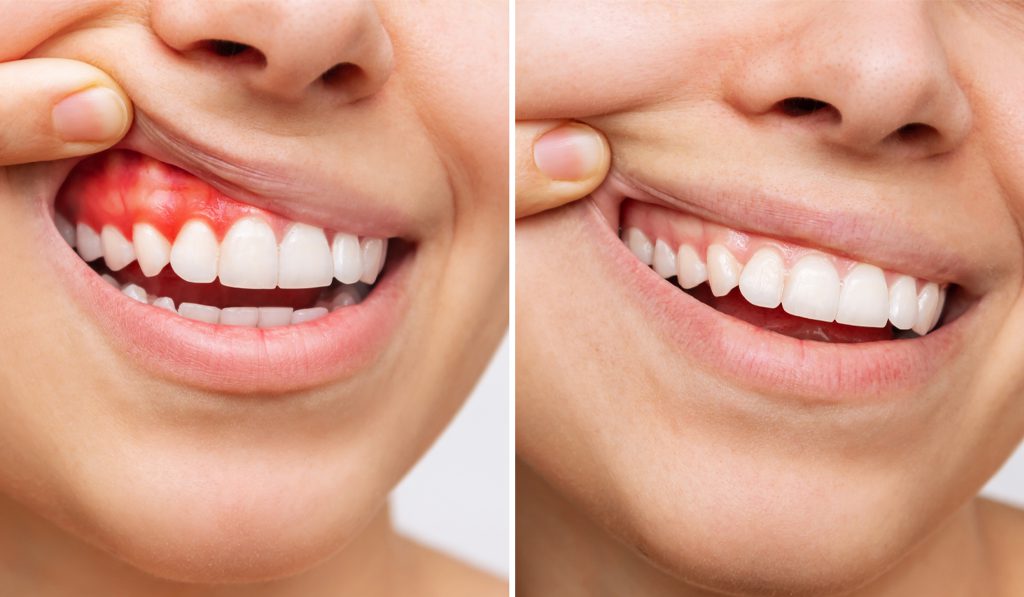
Bad oral hygiene can also lead to cardiovascular disease, which is why knowing the existence of periodontal diseases and taking effective preventive steps in advance is important. The mechanism in which the margin of the gum tissue covering the teeth wears away or draws back, revealing the root of the tooth is known as gum recession.
When gum recession happens, the “pockets,” or spaces are formed between the teeth and gum line, making it easy to build up bacteria that cause illness. The supporting tissue and bone structures of the teeth may be badly harmed if left untreated. This could ultimately lead to tooth loss.
Many individuals do not know that they have a gum recession as it happens slowly. Typically, the first symptom of gum recession is sensitivity to the tooth, or you may note a tooth appears longer than average.
Why Do Gums Recede?
There are a variety of variables that can contribute to the receding of your gums, such as:
- Periodontal Diseases: – These are bacterial infections of gums that damage gum tissue. This tissue supports bones to keep the teeth in place. The big cause of the gum recession is bad gum health.
- Your genes: – Some people may be more susceptible to gum diseases. In fact, studies show that 30% of the population may be predisposed to gum disease.
- Aggressive tooth brushing can trigger the enamel on your teeth to peel away and your gums to recede when you brush your teeth too vigorously or in the wrong way.
- Insufficient dental care: – Inadequate brushing, flossing, and antibacterial mouthwash rinsing make it easy for plaque to transform into a hard material called tartar that grows on and between your teeth. It can only be removed by a professional dental cleaning.
Periodontal Diseases
A more severe form of gum disease is periodontal disease. It is a disorder that causes swollen, irritated gums. It can ultimately lead to bone loss around the teeth if untreated.
The underlying jawbone (the alveolar bone) containing the teeth’s openings as well as the roots and tissue linking the tooth to the socket, may be affected.
- Dental caries: Dental caries are blisters or fractures of the teeth to the enamel and dentin (the layer under the enamel). There are some disturbing symptoms of bacterial species found in stable dental biofilm, which then contribute to dental caries.
- Gingivitis: This happens as plaque builds up and eventually leads to a bacterial infection of the gums. Undiagnosed gingivitis, which can also lead to tooth loss, can lead to periodontitis.
- Periodontitis: Infection/inflammation of the supporting systems of the teeth is characterized by periodontitis disease (e.g., periodontal ligament and alveolar bone).
As a consequence of gum disease, several hidden hazards exist in addition to such prevalent diseases. The symptoms of gum disease go beyond the teeth/gums, and the jawbone may be directly affected.
Relation Between Gum Disease and Jawbone Loss
Gum disease, also called periodontal disease, results in gum inflammation and is triggered by plaque and tartar bacteria. The gum disease can grow from gingivitis to a more serious type of periodontitis if the signs are untreated.
It can extend through the gum tissue and affect the jawbone as periodontitis progresses. The periodontitis would then infect the teeth-supporting jawbone as well as other tissues. As a result, when left weakened, the tooth may even fall out. This happens because the tissues will start to fail and the teeth may become loose.
What causes the loss of bone around your teeth?
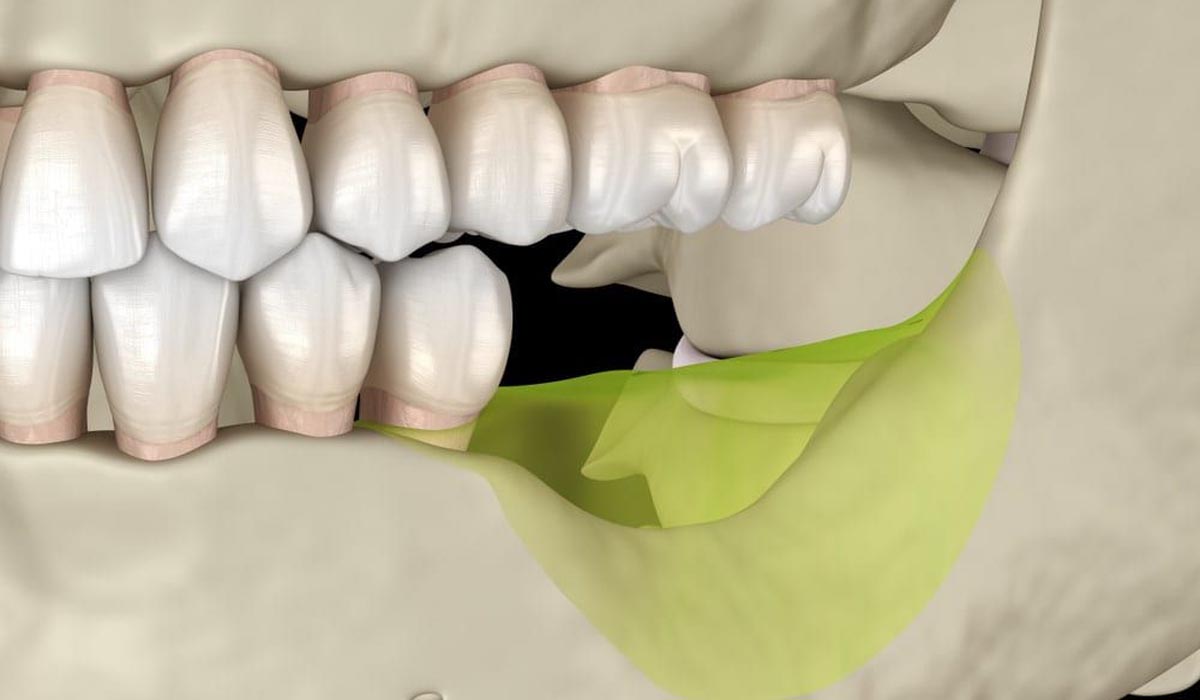
Periodontal disease, left unchecked, can cause inflammation that can spread to the bones below the gum line that maintain the structure of the teeth. The gums will start to recede, creating a space between the tooth and the gum where plaque will be stuck.
This will lead to loosening and dropping out of the teeth or the dentist needing to remove them. The bone supporting the teeth can be damaged as the disease grows.
Osteoporosis, tooth infections, and bacterial implant infections (peri-implantitis) are some other factors that cause bone loss around the teeth.
Nutrient Regime
Make calcium and vitamin D a priority. For bone health, calcium is critically essential. A study released by the Journal of Dental care found that 11 out of 17 studies revealed that osteoporosis (fragile bones) is linked with an increased risk of jaw bone loss.
Many calcium-rich foods in your diet, such as cheese, milk, spinach, watercress, and sardines or taking a calcium supplement, are used in order to help preserve bone density.
As it allows the absorption of calcium, vitamin D is also important for bone health. There are many foods that contain vitamin D, such as egg yolks; oily fish (salmon, mackerel, herring, and sardines); milk products, and meat products (liver and kidney).
- Stop smoking: Smoking increases the risk of periodontitis as it enhances the development of plaques and decreases bone mass. Smoking and age are significant risk factors for tooth loss.
- Eat a healthy diet: Gingivitis and bleeding gums can be caused by vitamin C deficiency. Eat foods high in vitamin C, such as peppers, broccoli, and kiwi. You can also take a vitamin C supplement as an alternative.
A 2017 review indicated that shortages of vitamin C, vitamin D, or vitamin B12 could be linked to the development and initiation of periodontal disease. In order to help develop healthy teeth and bones, have calcium-rich foods such as milk and cheese in your meal.
- Blood sugar control: One out of three people who have diabetes also have periodontitis. This happens due to high levels of blood glucose at some stage. Exercise can help lower the amount of blood sugar, and walking is a perfect way to start.
- Take probiotics: Recent studies have shown that not only do probiotics benefit your stomach, but can also assist with oral health. An analysis of 12 studies showed that the use of oral probiotics along with scaling by a dental hygienist is a healthy and effective way to treat periodontitis.
How can you avoid such diseases?
- Brush your teeth twice a day: Brush your teeth twice a day in the morning for 2 minutes with fluoride toothpaste. Also brush your teeth last thing at night, preferably with a small-headed toothbrush. To avoid gum and jawbone diseases, you should follow a strict oral health routine.
Brushing twice a day, flossing, and mouthwash should provide complete oral hygiene. When brushing, adopt the two-minute rule to make sure you are brushing day and night for two whole minutes.
- See your dentist regularly: You should visit your dentist every six months at least and, if necessary, see a dental hygienist for extra cleaning. Try to cut back on foods high in sugar along with this. You will need to urgently visit the periodontist if the gum disease has worsened.
The various treatment methods include flap operation, soft tissue grafting, and bone grafting. These therapies are recommended only when there is no other procedure to cure the disease of the gum and jawbone. If the jawbone disease has resulted in tooth loss, the dentist will have to install a dental implant.
It is only after the jawbone is healed that the treatment procedure will be carried out. When the infection spreads to other parts of the body, the healing process can be complicated. It is also recommended that any medication for gum and jawbone diseases should not be delayed.
- Floss before brushing: Everybody can clean their teeth once a day using floss or interdental brushes. If you have periodontitis, interdental brushes are preferred over floss because they do a good job of removing food debris and plaque between the teeth.
- Spit, don’t rinse: After brushing, most of us make the mistake of washing our teeth. This washes out the protective fluoride which improves the enamel of the tooth. It also decreases the amount of acid formed by the bacteria on the teeth.
You must be conscious of the preventive measures indicated above to Avoid Gum And Jaw Bone Diseases