Morning Sickness During Pregnancy
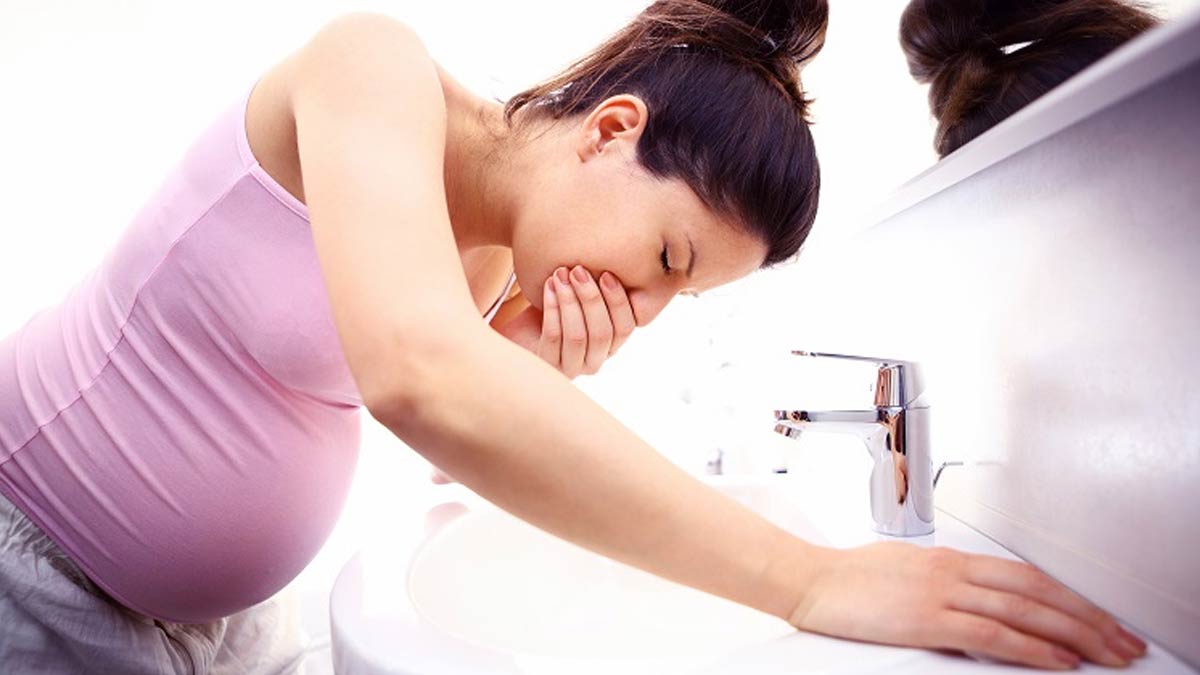
Nausea with or without vomiting is the most important discomfort which is seen with pregnancy. It is very common especially in the first months of pregnancy. Morning nausea is referred to as “morning sickness” in world literature. Despite the name, morning sickness can cause discomfort at any time of the day, it is often the first sign that a woman is pregnant. And it means the placenta is developing well. Mostly, nausea and vomiting are seen mildly and it gradually disappears after three months.
Nausea does not harm you and your baby and does not indicate that your baby has a problem. The absence of nausea and vomiting may also make some pregnant women worried about whether the baby is healthy or not. But this is not an indication of a problem with the health of you and your baby.
When Should I Call My Doctor?
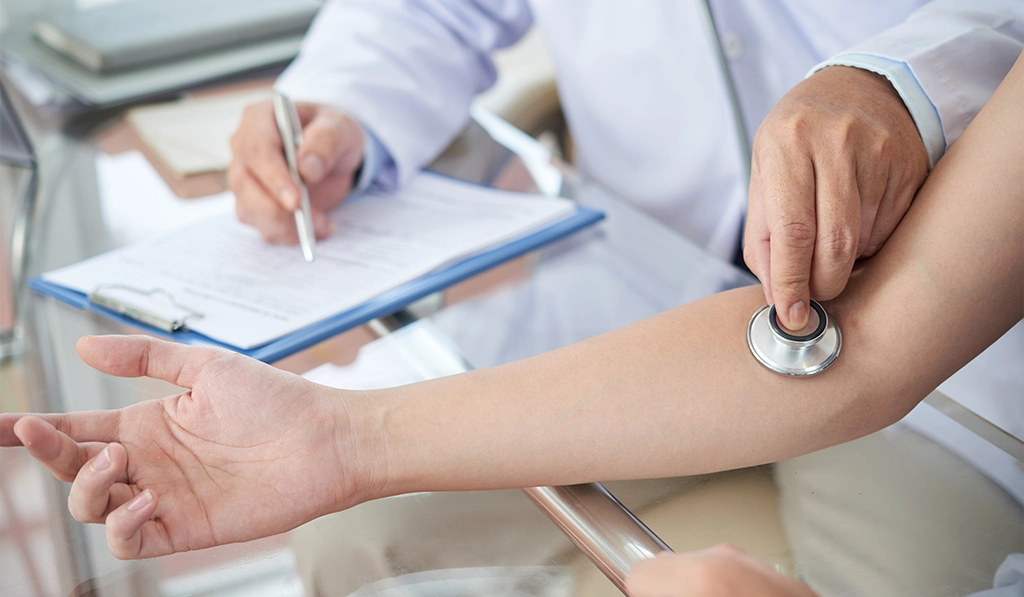
In some cases, nausea and vomiting can be very severe and may continue throughout the pregnancy. It is called hyperemesis gravidarum characterized by weight loss, possibly dehydration, and feeling faint that requires serious treatment and follow-up. In such cases, you should consult your gynecologist immediately.
CAUSES
The exact causes of hyperemesis gravidarum are unknown. Although there is still no single cause for nausea and vomiting during pregnancy in studies, one of the reasons is pregnancy hormones.
Risk factors are the first pregnancy, multiple pregnancies, obesity, and a history of eating disorders. The interesting thing is that nausea usually disappears in 3 months. This corresponds to the organ development period of the baby. Some studies show the psychological status of pregnant women as trigger factors.
Prevention
However, some researches show that cases of severe nausea and vomiting are less common in pregnant women who have been taking multivitamin supplements since the beginning of pregnancy. It is possible to ease nausea and make you feel better thanks to some precautions. For example;
- Stay away from the odours that disturb you.
- Increase the number of meals instead of eating heavy dishes in 3 meals a day.
- Take Snacks with high protein and dishes such as yogurt can be taken throughout the day.

- Take snacks such as saltines that will settle your stomach before getting off the bed.
- Avoid spicy, fatty, and sweet foods.
- Eliminate coffee.

- Drink water at least 30 minutes before or after solid food.
- Avoid lying down after eating.
- Consume ginger-containing foods.
- Take your prenatal vitamins before bed.
Ginger is a food supplement and its effectiveness has been proven by research.
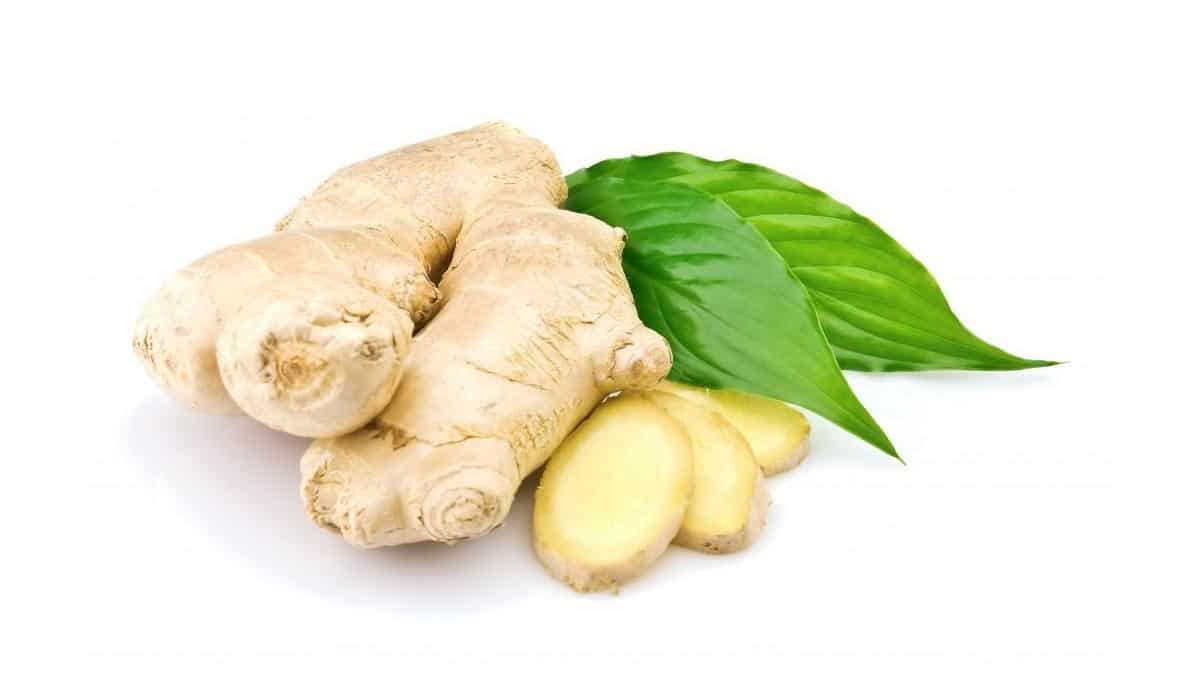

However, the most important point here is that you shouldn’t take any nutritional supplements, even if it’s herbal, without consulting your doctor.
Other Causes
Although nausea and vomiting are related to pregnancy, your doctor may investigate if there is another underlying cause, especially in severe cases. For example; such as molar pregnancy, thyroid diseases, and urinary tract infections. After eliminating all these causes, your doctor may recommend some medications based on ultrasound report and other medical reports.
Treatment
To make the pregnant woman who has nausea vomiting listen to her baby’s heartbeat during the examination since it relieves nausea for a short time.
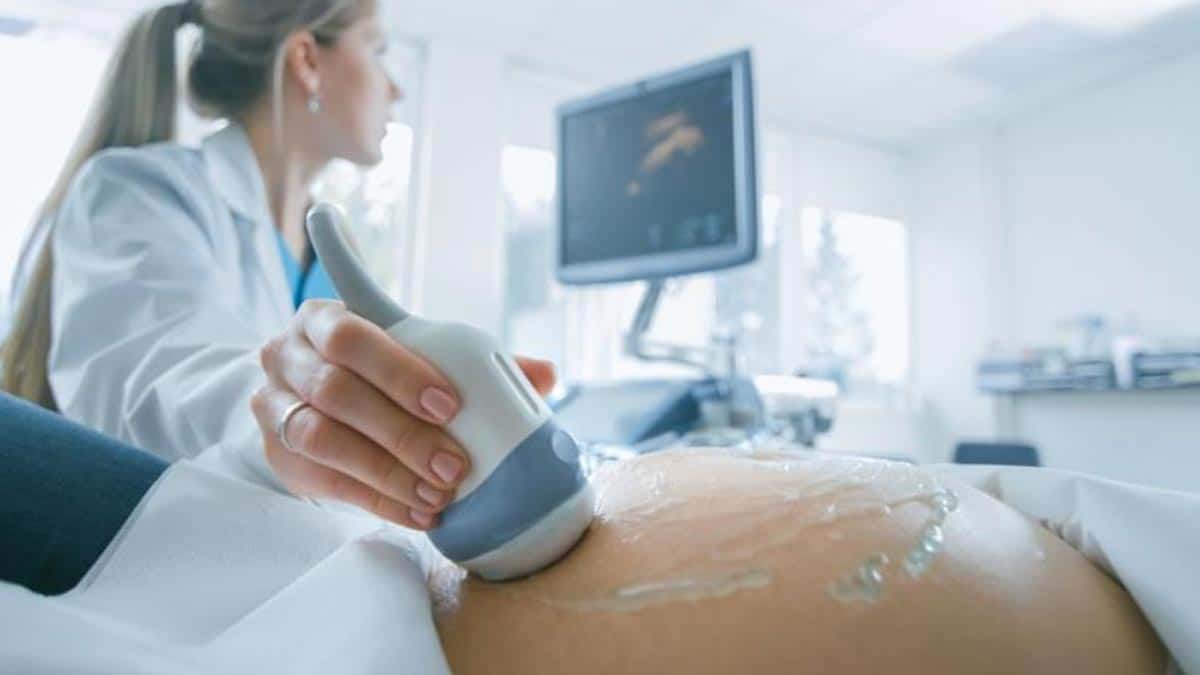
Management of women with nausea and vomiting during pregnancy depends upon symptom severity. First of all, the main approach includes dietary and lifestyle changes. Other important treatment approaches are medications and hospitalization for parenteral fluids in women with hypovolemia. During this period, you need to regularly visit your gynecologist.
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) may be recommended in the first step. Vitamin B6 is effective in easing nausea and has a good safety but it does not significantly reduce vomiting.

- There are anti-nausea medications that we can safely use during pregnancy, and these should never be taken without a doctor’s advice.
- Psychotherapy can be useful. If psychological sources of anxiety are identified, it may reduce the distress caused by nausea and pregnancy.
- Acupuncture has not been associated with any adverse effects on pregnancy outcomes and may help some women, even if a placebo effect.
Reference
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3676933/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27209471/
https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/practice-bulletin/articles/2018/01/nausea-and-vomiting-of-pregnancy
https://www.rcog.org.uk/globalassets/documents/guidelines/green-top-guidelines/gtg69-hyperemesis.pdf
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28629250/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27701665/